What is Node.js?
Why Node.js?
A common task for a web server can be to open a file on the server and return the content to the client.
Here is how PHP or ASP handles a file request :
- Sends the task to the computer's file system.
- Waits while the file system opens and reads the file.
- Returns the content to the client.
- Ready to handle the next request.
Here is how Node.js handles a file request :
- Sends the task to the computer's file system.
- Ready to handle the next request.
- When the file system has opened and read the file, the server returns the content to the client.
Node.js eliminates the waiting, and simply continues with the next request.
Node.js runs single-threaded, non-blocking, asynchronously programming, which is very memory efficient.
What Can Node.js Do?
What is a Node.js File?
- Node.js files contain tasks that will be executed on certain events
- A typical event is someone trying to access a port on the server
- Node.js files must be initiated on the server before having any effect
- Node.js files have extension ".js"
Install Node.js via NVM
Step 01
sudo apt-get update
Step 02
sudo apt-get install build-essential libssl-dev
Step 03
sudo curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/creationix/num/v0.33.11/install.sh / bash
If no curl
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/creationix/num/v0.33.11/install.sh / bash
Step 04
source ~/.profile
Step 05
nvm --version
Step 06
nvm install 6.16.0
Step 07
nvm ls
Step 08
node --version
Step 09
npm --version
What is a Module in Node.js?
- Consider modules to be the same as JavaScript libraries.
- A set of functions you want to include in your application.
Include Modules
- To include a module, use the
require()function with the name of the module
- Now you can include and use the module in any of your Node.js files.
Node.js as a File Server
Common use for the File System module:
- Read Files
- Create Files
- Update Files
- Delete Files
- Rename Files
Read Files
Create Files
The File System module has methods for creating new files:- fs.appendFile( )
The fs.appendFile( ) method appends specified content to a file. If the file does not exist, the file will be created:
Example:
- fs. open( )
The fs.open( ) method takes a "flag" as the second argument, if the flag is "w" for "writing", the specified file is opened for writing. If the file does not exist, an empty file is created:
Example:
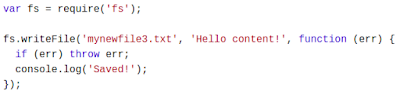
- fs.writeFile( )
The fs.writeFile( ) method replaces the specified file and content if it exists. If the
file does not exist, a new file, containing the specified content, will be created:
Example:
Update Files
The File System module has methods for updating files:
- fs.appendFile( )
- fs.writeFile( )
Delete Files
To delete a file with the File System module, use the fs.unlink( ) method.
- fs.unlink( )
Rename Files
To rename a file with the File System module, use the fs.rename( ) method.
- fs.rename( )
Upload Files
Step 1 : Create an Upload Form
Example :
var http = require('http');
http.createServer(function (req, res) {
res.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/html'});
res.write('<form action="fileupload" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">');
res.write('<input type="file" name="filetoupload"><br>');
res.write('<input type="submit">');
res.write('</form>');
return res.end();
}).listen(8080);
http.createServer(function (req, res) {
res.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/html'});
res.write('<form action="fileupload" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">');
res.write('<input type="file" name="filetoupload"><br>');
res.write('<input type="submit">');
res.write('</form>');
return res.end();
}).listen(8080);
Step 2 : Parse the Uploaded File
Example :- Include the Formidable module to be able to parse the uploaded file once it reaches the server.
- When the file is uploaded and parsed, it gets placed on a temporary folder on your computer.
var formidable = require('formidable');
http.createServer(function (req, res) {
if (req.url == '/fileupload') {
var form = new formidable.IncomingForm();
form.parse(req, function (err, fields, files) {
res.write('File uploaded');
res.end();
});
} else {
res.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/html'});
res.write('<form action="fileupload" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">');
res.write('<input type="file" name="filetoupload"><br>');
res.write('<input type="submit">');
res.write('</form>');
return res.end();
}
}).listen(8080);
http.createServer(function (req, res) {
if (req.url == '/fileupload') {
var form = new formidable.IncomingForm();
form.parse(req, function (err, fields, files) {
res.write('File uploaded');
res.end();
});
} else {
res.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/html'});
res.write('<form action="fileupload" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">');
res.write('<input type="file" name="filetoupload"><br>');
res.write('<input type="submit">');
res.write('</form>');
return res.end();
}
}).listen(8080);
Step 3 : Save the File
- When a file is successfully uploaded to the server, it is placed on a temporary folder.
- The path to this directory can be found in the "files" object, passed as the third argument in the parse( ) method's callback function.
- To move the file to the folder of your choice, use the File System module, and rename the file:
Example :
var http = require('http');
var formidable = require('formidable');
var fs = require('fs');
http.createServer(function (req, res) {
if (req.url == '/fileupload') {
var form = new formidable.IncomingForm();
form.parse(req, function (err, fields, files) {
var oldpath = files.filetoupload.path;
var newpath = 'C:/Users/Your Name/' + files.filetoupload.name;
fs.rename(oldpath, newpath, function (err) {
if (err) throw err;
res.write('File uploaded and moved!');
res.end();
}); });
} else {
res.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/html'});
res.write('<form action="fileupload" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">');
res.write('<input type="file" name="filetoupload"><br>');
res.write('<input type="submit">');
res.write('</form>');
return res.end();
}
}).listen(8080);
var formidable = require('formidable');
var fs = require('fs');
http.createServer(function (req, res) {
if (req.url == '/fileupload') {
var form = new formidable.IncomingForm();
form.parse(req, function (err, fields, files) {
var oldpath = files.filetoupload.path;
var newpath = 'C:/Users/Your Name/' + files.filetoupload.name;
fs.rename(oldpath, newpath, function (err) {
if (err) throw err;
res.write('File uploaded and moved!');
res.end();
}); });
} else {
res.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/html'});
res.write('<form action="fileupload" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">');
res.write('<input type="file" name="filetoupload"><br>');
res.write('<input type="submit">');
res.write('</form>');
return res.end();
}
}).listen(8080);









No comments:
Post a Comment